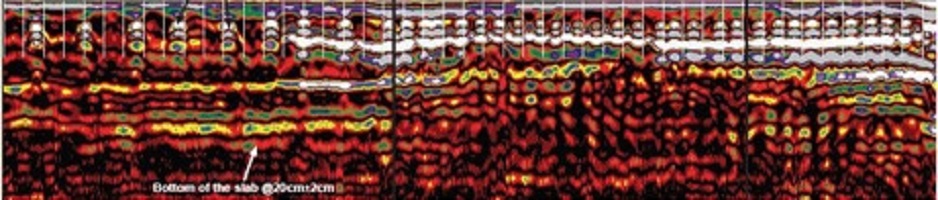
Structural Assessment
Rebar Spacing, Depth of Rebar and Slab Thickness Measurements
Structural assessment using Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) can provide accurate information to Engineers for determining the rebar spacing and depth of rebar in order to evaluate the structural integrity of the building if it is compliance with today’s building code.
In addition, GPR can also measure the thickness of suspended or slab-on-grade concrete slabs.
A sample of the GPR profile showing the Location and Depth of Rebar along with the Slab Thickness and Column Cap location.
Road Inspection
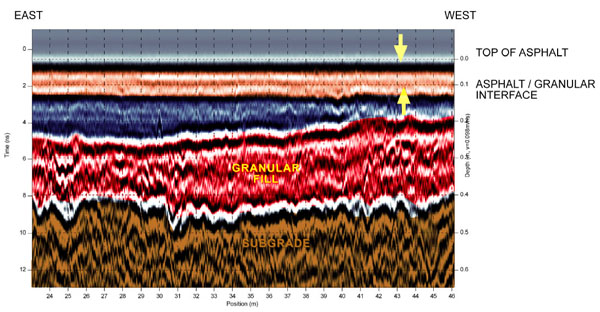
Due to the difference in the dielectric property of the asphalt and sub-base materials in road pavements, Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) has become an effective tool in the non-destructive evaluation of asphalt thickness and sub-base layers measurements. Acquisition of data is captured continuously, which provides a detailed profile of the road condition to Engineers for asset management and maintenance planning.
Void Detection
The presence of voids underneath the concrete slab poses instability to the structure under the designed loads condition. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) can determine the location of voids below the concrete slab due to changes in the property of the air-concrete interface. This non-destructive technique is often used in conjunction with other NDT methods, such as Impact-Echo to provide an accurate assessment of the void condition.
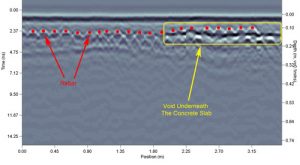
An example of a GPR profile showing the void location under the slab-on-grade concrete.
 A visual inspection of the void underneath the slab as determined with the GPR scanning.
A visual inspection of the void underneath the slab as determined with the GPR scanning.